A smart sensor is simply a sensor that can communicate to provide real-time diagnostic data and adapt based on that data. The data can be used to optimize a system, reducing costly downtime and increasing quality. Smart sensors are the backbone of today’s factory IoT network. Smart sensors, when paired with IO-Link, allow users to take advantage of the full range of capabilities of each sensor in your facility.
Smart Sensor Advantages
Smart sensors can deliver enormous advantages that impact decision-making and profitability. Three key advantages include:
Helping make better, data driven decisions: Smart sensors deliver visibility into the operational status of machine components (both historically and in real-time). And they allow plant managers to remotely monitor and diagnose systems quickly, as well as identify and resolve problems before the impact on machine availability and productivity compounds.
Maximizing uptime: Predictive analytics allows for more accurate planning of machine maintenance, which can help maximize uptime, increase mean time between failure (MTBF), and reduce costs of unnecessary preventative maintenance and spare parts inventory.
Increasing productivity: Interconnectivity enables seamless communication among machines, components, and people, increasing productivity. It also increases efficiency by allowing for more autonomous machine performance and streamlined manual processes.
The Future Of Maintenance, Using Smart Sensors And IO-Link
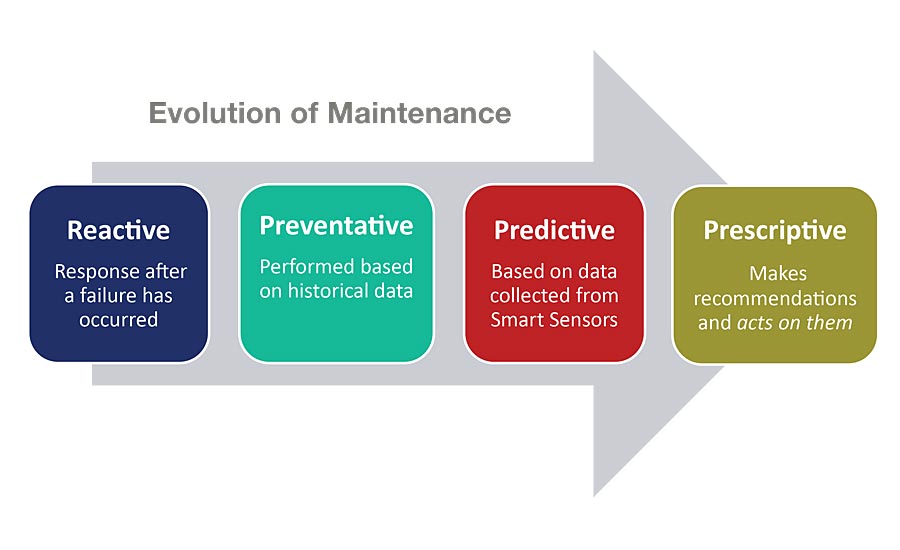
Maintenance operations have come a long way since the days of reactive maintenance, when technicians became aware of a problem only after the machine had malfunctioned. The next step was preventative maintenance, which is routine maintenance, based on historical data and performed to head-off likely future problems. Then came predictive maintenance, which is based on data collected from smart sensors. This type of maintenance doesn’t replace things that might go bad in the near future, it uses real-time data to provide warning of a gradually building problem. With predictive maintenance, you aren’t replacing good components that have lots of life left in them, but instead replace them only when truly needed. The next step in the evolution is prescriptive maintenance. Prescriptive maintenance not only alerts the operator of a problem, but it recommends or prescribes the maintenance step to fix it. And in some cases, that prescription can be automatically implemented.
A sensor, monitoring bulk-solids flow, is mounted remotely in a dusty location. Gain data identifies that the sensor lens is getting dusty and will need cleaning. Alerts are sent out notifying the maintenance team of the problem. And an air-purge can be programmed for an automatic triggered, clearing dust from the sensor.
Smart Sensors And IO-Link
Smart sensors, paired with IO-Link, allow users to take full advantage of all the benefits they can offer. IO-Link is the first standardized IO technology for communication with sensors, lighting, and actuators.
IO-Link provides:
- A standardized communication technology
- Point-to-point communication that can work with any fieldbus
- Bi-directional communication
IO-Link provides three layers of communication: plant communication, control communication and device communication. System components include IO-Link-enabled devices, such as sensors, indicators, and actuators; an IO-Link hub, which allows non-IO-Link device data to be communicated; an IO-Link master: an interface to industrial protocols; and cabling (standard, 3-wire, non-shielded cable, up to 20 meters in length).
Adding IO-Link
As of 2018, there were nine million, and growing, IO-Link enabled devices in the field. IO-Link is an open standard protocol and requires only a master to integrate IO-Link enabled devices into the system. IO-Link makes the sensors appear like EtherNet / IP, PROFINET, EtherCat enabled devices on the network. The IO-Link data is communicated to the PLC just like other ethernet-enabled devices.
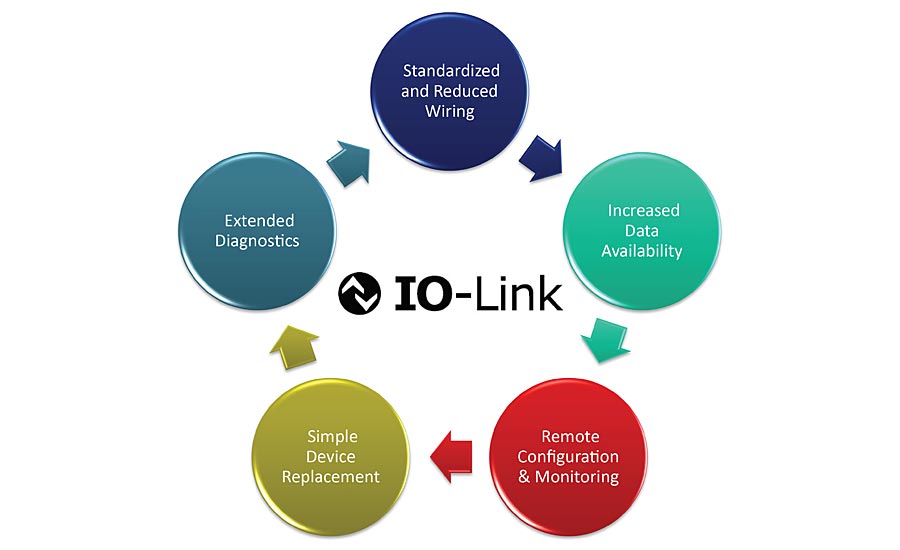
The 5 Advantages of IO-Link
1: Reduces Costs By Using Standardized And Less Wiring
- Standard M12 or M8 connections reduce the number of needed cables in spare parts inventory to length variations only. Shielded cables are not required and installation time is minimized.
- Replaces analog signals: Eliminates special I/O cards and cables. Higher precision analog value avoids D/A and A/D conversions.
- Has ability to further reduce wiring using an IO-Link enabled hub I/O block to integrate simple non IO-Link enabled devices.
2: Increases Data Availability
- Access to sensor-level data brings powerful insights via continuous data monitoring and status diagnostics. Devices easily produce data for IIOT and Industry 4.0 efforts.
- IO-Link allows three primary data types: process data (cyclic), parameter data (acyclic) and event data (acyclic).
3: Allows Remote Configuration & Monitoring
- Enables remote device parameter reading and programming.
- Allows fast configuration and commissioning: Users can copy configurations between multiple devices without need for target to be present to teach sensor.
- Permits users to dynamically make changes from the control system and lets them adjust for target variations and faster product changeover.
- Lets users monitor and diagnose connection and device status, so decisions are based on real-time data.
4: Reduces Or Eliminates Downtime
- Allows users to import stored parameter values into a replacement device via Auto-Device Replacement (ADR), which eliminates manual parameter setting for a new device, minimizing downtime and reducing risk of error.
5. Extended Diagnostics
- Lets users establish alarms and preventative and prescriptive maintenance tasks based on real time information. Example uses include:
- User resettable runtime to schedule standard maintenance
- Excess gain to identify sensor needs cleaning
- Discovery function to indicate which sensor needs attention
- Total runtime predicts when to replace device
Predictive maintenance employs the use of sensors to precisely collect data describing an asset’s condition and overall operational state. The data can then be analyzed to predict when failure events will occur.
Prescriptive maintenance takes this analysis a notch higher by not only predicting failure events, but also recommending actions to take. Potential outcomes when such recommended actions are performed are then calculated and anticipated.
- Maximizes OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness)

Prescriptive Maintenance: The sensor on conveyor 2 alerts the operator that its lens needs cleaning before it fails.
Conclusion
Smart sensors provide real-time diagnostic data and adapt based on that data to optimize a system, reducing downtime and increasing quality. These sensors drive the factory IoT network and Industry 4.0. Using smart sensors brings advantages that improve decision-making and profitability. And pairing these sensors with IO-Link allows users to take advantage of the full range of capabilities of each sensor in your facility. These advantages include allowing better, data-driven decisions, remote programing, reduced downtime, and extended diagnostics.



