When determining which borescope is appropriate for a given application, consider the workpiece factors such as possible defect size, entry port size and area needing inspection. Environmental factors such as working temperature and pressure will determine the level of robustness required from a borescope.
Rigid borescopes are generally used when the path between the operator and the area being inspected is a straight line. The basic components of a rigid borescope are a tubular shell, eyepiece, optical lens, viewing head and light source. An optical train consisting of the objective lens, relay lens and eyepiece lens brings the image to the operator. The viewing head determines the direction of the view; common viewing head designs are right angle, circumference, bottoming, forward oblique and retrospective. Illumination is achieved by either an incandescent lamp or fiber optics.
Flexible borescopes, or fiberscopes, are generally used when the path between the operator and the area being inspected is not a straight line. The basic components of a flexible borescope are fiber bundles, objective lens, protective sheath, eyepiece lens, focus and diopter ring, articulation controls, and an auxiliary light source.
A flexible borescope can have as many as 40,000 glass fibers, each consisting of a central core of optical glass coated with a layer of cladding of a different glass with a different reflective index. Each flexible borescope will contain two bundles of fibers. One connects with the light source and illuminates the object under inspection, and the other brings the image to the eyepiece. Both bundles are housed in a protective conduit of flexible stainless steel. Flexible borescopes will usually have an articulating tip, adjustable objective lens and a choice of viewing heads.
Videoscopes, incorporating a probe, video processor and display, can be rigid or flexible. An electronic sensor at the tip of the probe transfers the image electronically to the processor. Besides producing video images, videoscopes can produce still images as well, and images can be recorded for review or permanent documentation. Furthermore, software packages for use with videoscopes help streamline inspection through their ability to automate reporting and store data to a centralized database.
What follows are borescope product offerings available today.


The MicroRigid has a solid glass rod lens that runs the entire length of a stainless steel probe. It offers high image quality and straight in-line access to the inspection area for observing fine cracks, sharp edges and minute defects. The scopes attach to digital video documentation systems. Both designs also use the same interchangeable quick focusing eyepiece that adjusts to the operator’s vision.


In addition to the videoscope and monitor, the system comes with storage for four viewing tips, a CD/DVD drive, an integrated light source and storage for a battery.

The industrial videoscopes are fully dust-proof, rainproof and drop-proof up to 1.2 meters. They also have a compact body about the size of a small computer bag.
The IV8635X1 has object retrieval tools that can attach to the end of the scope. In addition to performing conventional tasks such as visual inspection and measurement, the tools increase the versatility of the scope, enabling the operator to retrieve foreign or fallen objects.
The IV8000-2 is equipped with an outdoor-use, daylight-view LCD monitor, which can display clear images even under strong sunlight. The addition of ImageNotepad to the IV8000-2 also enables the operator to enter comments on recorded images for the creation of reports.

The videoscope provides high-quality imaging with easy tip manipulation, digital recording and annotation. The videoscope is standard with a rugged tungsten insertion tube for maximum durability.

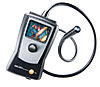




Powered by a lithium ion battery, the videoscope is cordless and has no tethers. Its compact design and shipping case is small enough that it can be classified as carry-on luggage. The system’s tungsten braided insertion tube has 360-degree articulation.
LED light is routed through a fiber optic bundle, projecting the inspection image onto a high-resolution LCD screen. Interactive operator menus make navigation intuitive.
Designed to withstand harsh environments, the videoscope is housed in impact-resistant polycarbonate, and makes use of double threaded optical tips to eliminate the risk of foreign object damage.
Inspection results are captured as high-resolution images or MPEG4 video for analysis or collaboration. USB data ports for flash memory thumb drives enable additional data storage.


The QualiEyes I portable LCD videoscope has a 2.5-inch color LCD display, 300,000-pixel image sensor and an LED light source. The gooseneck insertion tube has a diameter of 0.39 inch and is 8.2 feet in length. The videoscope can operate for 48 hours under continuous use. Images can be stored and moved to a PC for further inspection. They also can be transmitted directly to an external monitor for group analysis of real-time images.
The QualiEyes II industrial fiberscope has a built-in LED light source, high-resolution image bundle and an optical system with a depth of observation between 1.2 inches and 5.9 inches, along with a working length of 51.2 inches. The built-in LED light source has a lifetime of 100,000 hours.