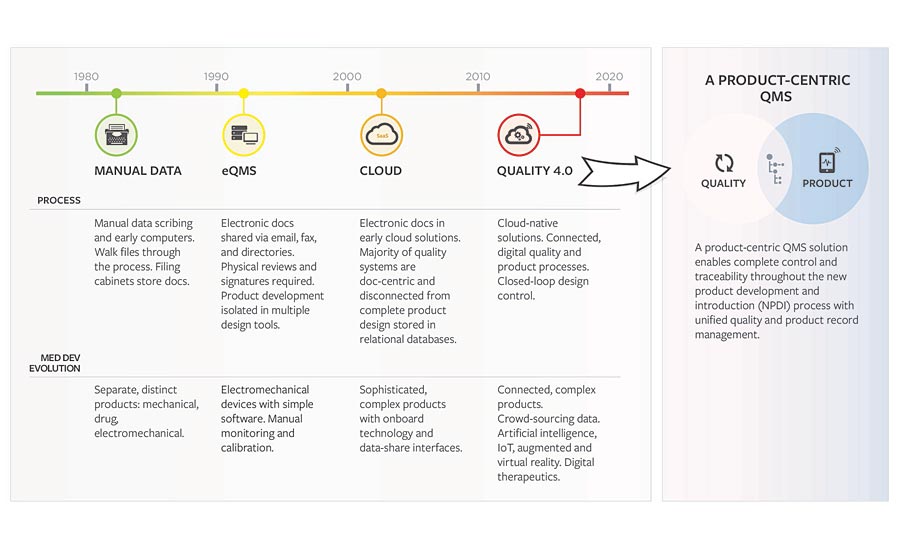
Quality 4.0 derived from Industry 4.0, also known as the fourth industrial revolution. Prior to the fourth revolution, the first revolution started with machine manufacturing, steam power, and the move to cities by agriculturalists. In the second industrial revolution, production was automated and mass manufacturing cut the cost of consumer and industrial products. The third revolution involved the use of electronics and control systems in manufacturing, which helped drive down costs and resulted in increased product complexity and lower product costs. Today’s fourth industrial revolutionary change is driving new quality paradigms, processes, and technologies (https://blog.lnsresearch.com/quality40).
In the medical device manufacturing market, in particular, there are numerous challenges to design and produce safer devices. Regulatory requirements are just one component—but incorporating emerging and continually evolving technologies requires device companies to raise their game if they want to stay ahead of the competition and leverage cutting edge technologies—from the Internet of Things (IoT) to artificial intelligence and machine learning to augmented reality and even robotics. Quality 4.0 is the convergence of these new technologies that make up the manufacturing landscape.
Technology to Reshape the Market
Industry 4.0 represents the dawn of the digital transformation having begun with the third revolution, connecting the physical and natural worlds. The impact of digital data, analytics, connectivity, scalability, and collaboration are the drivers empowering this fourth industrial revolution and informing Quality 4.0 strategies. As we find new ways to connect people, devices, and data, the democratization of technologies is introducing transformative capabilities in analytics, material science, and connectivity. For the medical device industry, such technologies empower a quality transformation of culture, leadership, collaboration, and standards (https://blog.lnsresearch.com/quality40).
Quality 4.0 is reshaping device designs, functionality, manufacturing processes, supply chain strategy, customer service, and the methods of maintaining quality systems that are compliant with regulatory bodies like the FDA and ISO. Intelligent and connected technologies are rapidly becoming more widely used as manufacturers seek an advantage to introduce inventive products to market and leapfrog existing competitors.
The Move to Digital
MarketsandMarkets forecasts the medical device market will grow to $63.43 billion by 2023. Smarter, more automated, and connected devices are improving the state of healthcare, making it possible to perform remote surgeries with doctors on the other side of the globe. Medical device companies’ ability to leverage Quality 4.0 technologies will be key to market success in the years ahead. LNS Research sees Quality 4.0—the application of Industry 4.0 technologies to quality initiatives—as following in IoT’s path. In fact, industry experts have determined that a quarter of medical device manufacturers’ digital transformation technologies drive quality improvements. These same technologies are being used to design and deliver products. What does this mean for medical device manufacturers?
For starters, digital transformation trends have helped define Quality 4.0 strategies to eliminate reliance on disparate paper-based quality management systems and processes. The move away from manual systems reduces errors, silos, collaboration barriers, and traceability issues. Furthermore, the digitization and automation of design and production processes enables small and global companies to scale their design and supply chain processes quickly. For instance, one such company, RefleXion Medical, a leader in biology-guided radiotherapy systems for cancer treatment, knew they needed to implement a completely connected QMS that could scale to support their path to digital transformation and improved compliance. They required a flexible platform that could grow with their team, products, and path throughout the quality compliance process.
Newer Quality Standards along the Supply Chain
In order to speed products to market, today’s medical device manufacturers rely on distributed teams and supply chains, including contract manufacturers, design partners, and tiered component suppliers. Companies that have embraced new technologies and cloud-based systems understand the unique benefits that digital transformation technologies can bring to a device manufacturer’s product requirements, product capabilities, and regulatory compliance objectives.
In the life sciences realm, digital therapeutics, medical diagnostic equipment, implantable devices and disposable devices are just a few of the wide array of devices that strive to be problem-free while delivering higher throughput and maintaining compliance.
Integration with Connected Teams
Using a connected, or more product-centric quality management system (QMS) can help to meet the demands created by Quality 4.0 trends. As complexity of products increases with AI, IoT, robotics, and related 4.0 technologies, quality teams must have a unified system to identify issues, address audits, and resolve quality incidents. This ensures that the full, complex product design comprised of electrical, mechanical, and software components is contained within a single system.
This foundation allows for complete, connected quality and corrective action records and provides increased visibility and transparency as teams collaborate through each phase of new product development and introduction.
Medical device companies will gain competitive advantages by having more intelligence-driven product and quality process insights. This, in turn, will lead to better data-driven decisions and cross-functional visibility with quality, engineering, operations, and supply chain teams. These Quality 4.0 transformational technologies add complexity in meeting strict medical device requirements:
- ISO quality system requirements
- Complaint management and corrective action preventive action (CAPA)
- FDA 21 CFR Part 820
- FDA 21 CFR Part 11
- ISO 13485
- To ensure compliance, a product-centric QMS solution makes it possible to:
- Create a completely connected quality and product process
- Establish quality product processes to avoid audit issues
- Ensure traceable design and change controls
- Manage product bills of materials linked directly to quality records
- Drive closed-loop quality and CAPA processes to faster resolution
- Improve quality compliance and supplier management processes
The last point about supplier management process is essential because the right QMS solution can unify quality and product record management to provide complete control and traceability, simplify audits, and decrease risks.
Use Cases from Device Makers
Swan Valley Medical is a manufacturer of surgical instruments and accessories for applications in the field of urology. They were burdened with inefficient paper-based manual processes that resulted in potential compliance exposure due to misplacing critical documentation. During audits, when missing or inaccurate information was found, it was difficult to recover and could take hundreds of hours or even several months.
With a cloud-based product-centric QMS solution, accelerated root-cause analysis and risk management observation processes were implemented. This enabled different processes to connect with others through linked product and quality records, thus supporting audits with cross-linked evidence chains.
Closed-loop CAPA processes help quality teams identify, analyze, and resolve quality issues faster. In one example, Pulse Biosciences deployed a closed-loop quality system across its organization. All team members were able to work collaboratively on the most current product definition and latest quality records with a product-centric QMS. With streamlined CAPA processes, Pulse Biosciences was able to address urgent corrective actions rapidly with better audit trails.
Kinsa offers the first FDA-cleared, doctor-recommended smart thermometers. They implemented product-centric QMS to assist in the design of the company’s first-ever connected device. The application of Quality 4.0 technologies has helped Kinsa revolutionize how healthcare can be reimagined in an IoT universe through connected technologies to streamline product development, improve quality management, and shorten the time to resolve customer issues.
Keeping up with Quality 4.0
The march to deliver more intelligent devices is moving ahead at full speed. Both large, established medical device companies and smaller innovators are racing to improve healthcare by connecting people and data using newer technologies like IoT, AR, and robotics to deliver better outcomes to patients around the globe.
The advances made with Industry 4.0 have helped drive Quality 4.0 technologies and strategies to improve quality compliance. The ability to align complex product development and quality processes is critical to compete in today’s global economy. We not only develop products virtually with distributed teams, but we now have the ability to heal and perform surgeries where doctors and patients are separated by multiple time zones with intelligent robotics and augmented reality devices.
So, consider your goals and realities for creating and delivering complex products that meet regulations from the FDA to ISO. Make sure you can create a completely traceable, reduced-risk environment to protect your patients as well as your profits and long-term viability.
Quality 4.0 trends require smarter, connected strategies to ensure your company isn’t left behind.